FAQ
1. How do I get on your FTP?
They are not my FTP's other
people have submited their ftp servers into a automated list. I do not
take credit or responsibility for anything you may find or trade on these
sites.
2. OK OK. How do I get on their FTP?
I recommend using a ftp
client like cuteftp.
3. Where do I get cuteftp?
CuteFTP can be downloaded form http://www.cuteftp.com/
4. How do I use cuteftp to get stuff from ftps?
Cuteftp has a
great feature that simplifyes everything greatly. You just have to make
sure it is set to monitor the clip board. To do this:
1) Open
cuteftp
2) Close the site manager if it opens (the ftp list)
3)
Click Edit from the menu
4) Click Settings
5) Click Advanced
6)
Make sure there is a checkmark beside the "Monitor clipboard for FTP URLs"
feature
7) Click OK
8) Thats it as far as setting it up.
Make
sure that cuteftp is running in the background while you goto my site.
Then when you find a site you would like to visit just right click on its
link and select "Copy Shortcut" from the popup menu. Now bring cuteftp to
the top of the desktop. You should have noticed that cuteftp has connected
to a server or is trying to. Once it connects a prompt should popup with
an OK button. READ IT this is where the webmaster of the ftp will put
important information such as how to get an account or the ratio for the
account you are already using. Thats it your on!
5. How do I get files from a ftp?
After you have connected to
the ftp read any readme.txt files on the server (usually these files are
free to download without having to upload first).
Assuming you are
on a ratio site you will have to upload some files first before you will
be able to download anything. A 1/2 ratio means that if you upload 1meg
you will then be able to download 2megs. Some ftp servers go by number of
files so that a 1/2 ratio means that you would have to upload 1 file of
any size and you would be able to download 2 files of any size (this
method isn't used very often).
Another type of setup is a passowd
hunt. In my opinion they suck but hey they are also quite popular. Anyway
with this type of account you usually have to hunt for a password on some
web site that the ftp webmaster makes money off of every person who visits
it. And then that password you hunted for is the one you can use to log
back onto the ftp and get a leech account (although sometimes its just a
ratio account).
6. I uploaded a bunch of stuff but was disconnected now it says I
have not uploaded anything.
Thats right once you logoff or are
disconnected your credits are erased on most FTP server. If you email or
ICQ the webmaster of the site s/he might give you your own account but I
wouldn't hold my breath.
I hope that clears some things up!
How do I create my own FTP
server?
We will be using Serv-U for this how to.
Serv-U can be downloaded form http://www.serv-u.com/
At the end of the software installation they will be a check mark in
"Start Serv-U Administrator program" so just leave the check mark in that
box, it will bring you to a tutorial on how to set it up
1. Click next a the first dialog box
2. It then asks if you want to enable small images for the menu
this is up to you. Click next
3. Click next again
4. Your IP address, leave the IP address blank. Click next
5. Domain name, here you can put anything that you would like to
call your site. It is completely up to you. After you chose the name.
Click next.
6. Anonymous account, it asks if you would like to allow anonymous
access. If you choose yes, you will not have to worry about user name and
password. But I recommend choosing no, that way you will be able to
specify who has access to your site and what the restrictions on those
users are. Put the dot in no. Click next
7. Named account, leave the dot in yes. Click next
8. Account name, chose a login name this will be use by the people
trying to access your site. I highly recommend a single word without
capital letter, like "test". After entering the name. Click next.
9. Account password, this is the password the user will have to
enter when accessing your site. To make it easier for the user I recommend
using the same as the user name. In my example I use "test". Click
next.
10. Home directory, now chose a directory that the user will see
when accessing your site. I suggest making a directory especially for that
use like "C:\ftpserver. Click next.
11. Lock in home directory, this is completely up to you but I
suggest you chose to lock the user in the home directory (by putting the
dot in yes). Click next.
12. Admin privilege, I recommend leaving it as "no privilege".
Click next.
13. You are almost done but I suggest changing a couple of little
things. Open "Serv-U Servers" by clicking the + (if not already done) then
open "<< Local Server >>" then "Domains" then "this is the
name you choose in step 5" then "User" then "the name you choose in step
8" you will see that on the right there is a new panel. You should go to
"Dir Access" by clicking the appropriated tab. You will see the folder
that you previously choose in step 10, I highly recommend that you click
that folder and remove all the check mark in Write, Append, Delete,
Create, Remove and Inherit. Look at the following picture it should help.
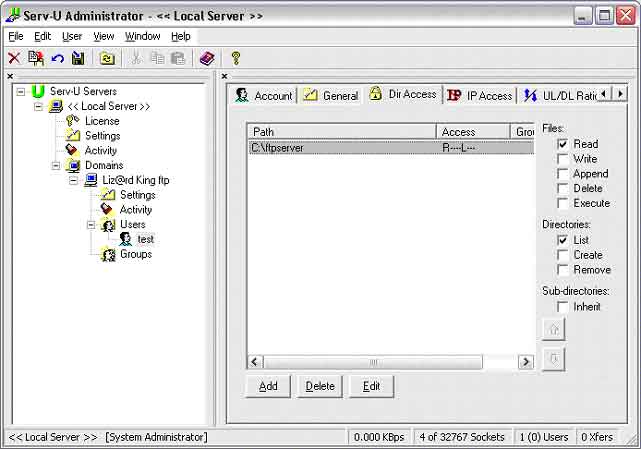
14. Downloads: Now created a download folder. You should create that
folder in the folder previously created in step 10 I suggest calling it
"ftpdownload", so is path should be "C:\ftpserver\ftpdownloard". Now click
add and choose that folder. You should change the proprieties of that
folder to "Read", "List" and "Inherit". See picture
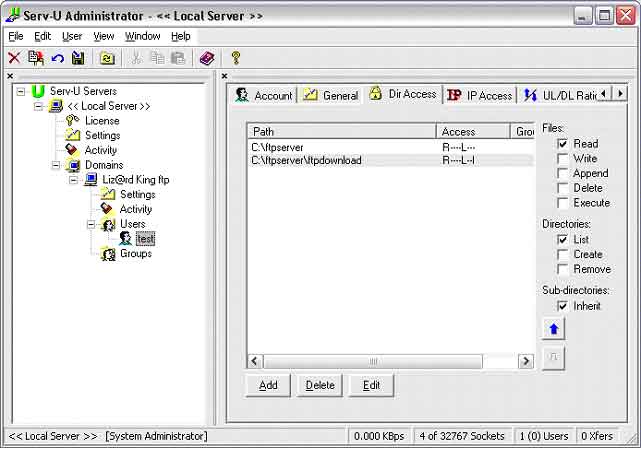
15. Uploads. Now created an upload folder. You should create that
folder in the folder previously created in step 10 I suggest calling it
"ftpupload", so is path should be "C:\ftpserver\ftpupload". Now click add
and choose that folder. You should change the proprieties of that folder
to "Read", "Write", "List", "Create" and "Inherit". See picture.
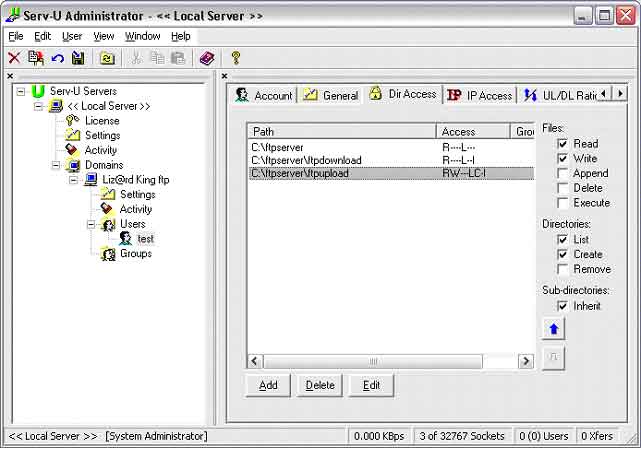
16. Ratio. Now click the UL/DL Ratio tab to set ratio. Put a check mark
in "Enable upload/download ratios". I suggest putting the dot in "Count
bytes per session" and a ratio of "1 to 2". See picture
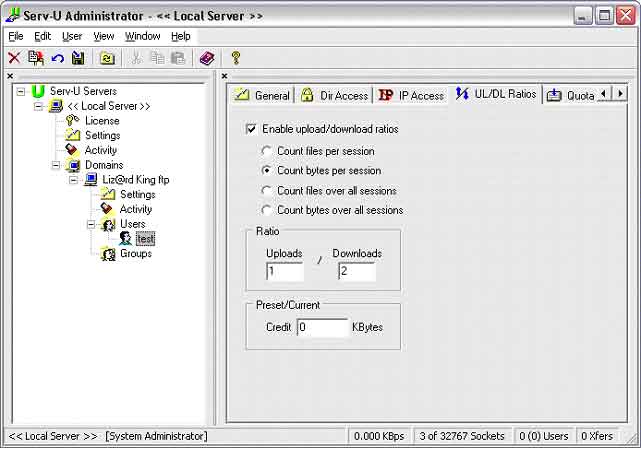
17. Now the only thing you need to do is find your IP address and
summit your site. To find you IP address simply click Help and click Local
IP Address and you should see a number and that number is your IP
address.
Written by The Liz@rd King (MichaŽl Rioux)
GLOSSARY
ANONYMOUS
A way of logging on to servers as a guest, which
gives you limited access to that server. Many FTP sites allow you to login
anonymously in order to download files. Directories or files requiring a
secure User ID and Password will not be accessible.
ASCII
American Standard Code for Information Interchange.
This is the basic clear-text Latin characters. There are 128 standard
ASCII codes, each of which can be represented by a 7 digit binary number:
0000000 through 1111111.
ADSL
Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line. Delivers and
receives information on current telephone lines at higher bandwidth
speeds. ADSL is a new form of Internet connection rapidly growing in the
US.
BAUD
The "baud rate" of a modem is how many bits it
can send or receive per second. Your modem uses this measurement to tell
you what speed you are connected at or transferring.
BETA
The second stage a software program goes through before
a final is released. Software undergoes rigorous testing until it is ready
to be released.
BINARY
A numeric system that represents all numbers using
only two digits: 1 and 0.
BIT
The basic unit of information in a binary numbering
system. A computer detects the difference between two states (high current
and low current) and represents these two states as one of two numbers (1
or 0).
BANDWIDTH
The range of frequencies a channel can carry. The
higher the frequency, the higher the bandwidth and the greater the
capacity of a channel. In Internet terms, higher bandwidth means a higher
ability to transmit and receive data.
BPS
Bits per second. The amount of data that can be
transmitted over a digital line.
BROWSER
A program used to view, download, upload, surf or
otherwise access documents (pages) on the World Wide Web. Popular Web
browsers include Netscape and Internet Explorer.
BYTE
A series of 8 bits, which represent a single
character.
CLIENT
A remote computer connected to a host or server
computer. Also refers to the software that makes this connection possible,
such as an FTP client.
DNS
Domain Name Server. Specific software that
runs on a server and resolves domain names to actual IP addresses. Nodes
communicate with each other using IP addresses rather than domain names,
though users may never see the actual IP addresses being used.
DOMAIN NAME
The "address" or URL of a particular Web site.
You can register your own domain name at www.networksolutions.com.
Domain extensions vary depending on the site in question:
- COM - An Internet domain used for business or commercial ventures.
- EDU - An Internet domain used for educational facilities.
- GOV - An Internet domain used by the government.
- MIL - An Internet domain used by the military.
- NET - An Internet domain used for network businesses.
- ORG - An Internet domain used for non-profit organizations.
DOWNLOAD
To copy a file from a remote computer to your
computer. There are a few methods of doing this on the Internet. HTTP, FTP
and e-mail attachments are the most common.
E-MAIL
Electronically transmitted mail. E-mail
sends your correspondence instantaneously anywhere in the world via the
Internet. It is the most popular use of the Internet because of the
capability to send messages at anytime, to anyone for less money than it
would cost to mail a letter or call someone on the phone.
ETHERNET
One of the most common local area network (LAN)
wiring schemes, Ethernet has a transmission rate of 10 megabits per
second; a newer standard called Fast Ethernet will carry 100 megabits per
second.
FINGER
Software that allows you find out more information
about an Internet user, such as their real name and if they are logged in
at the present moment.
FIREWALL
A firewall is a safeguard utilized by many Local
Area Networks (LANs) or Wide Area Networks (WANs) to protect the network
from unauthorized access from the outside. They are basically gates that
verify the users before they leave or enter the network by way of a User
ID, Password or IP address.
FTP
File Transfer Protocol. A standard protocol for
transferring files between remote computer systems. Until recently, it was
used almost exclusively on UNIX workstations and mainframes, but after PC
users gained access to the Internet it became a popular alternative to BBS
systems. The biggest limitation was that FTP-compliant software usually
used a command line interface, which wasn't easy for beginners to work
with. As the Internet grew in popularity, new standards appeared (Gopher,
WWW), providing more user-friendly front-end software. FTP, however, still
remains the popular choice among power users and computer professionals.
GATEWAY
A computer system for exchanging
information across incompatible networks that use different protocols. For
example, many commercial services have e-mail gateways for sending
messages to Internet addresses.
HOST
A computer that is setup to allow connections
from other machines (known as clients).
HOST ADDRESS
The Internet IP Address or hostname of a remote
server.
HTML
Hypertext Markup Language. The language used to create
and design Web sites. HTML is a standard text file with specific tags that
a browser reads and interprets into a Web page.
HTTP
Hypertext Transfer Protocol. A protocol that your Web
browser uses to connect to and receive data from Web servers.
INTERNET
Originally designed by the U.S. Defense Department
so that a communication signal could withstand a nuclear war and serve
military institutions worldwide, the Internet was first known as the
ARPAnet. The Internet is system of linked computer networks, international
in scope, that facilitates data communication services such as remote
login, file transfer, electronic mail and newsgroups. The Internet is a
way of connecting existing computer networks that greatly extends the
reach of each participating system.
INTRANET
A private network inside a company or organization
that uses the same types of software that you would find on the public
Internet, but is only for internal use.
IP ADDRESS
Internet Protocol Address. A numeric address that
is given to servers and users connected to the Internet.
IRC
Internet Relay Chat. A live chat area of the Internet in
which real-time conversations among two or more people take place via
special software. Each specific IRC channel begins with a # and is
dedicated to a different area of interest. IRC is considered another part
of the technology of the Internet the same way FTP, Telnet and the Web
are.
ISDN
Integrated Services Digital Network. Provides a fast,
commercially available link to the Internet. ISDN is a set of
communications standards allowing a single wire or optical fiber to carry
voice, digital network services and video.
ISP
Internet Service Provider. A company that provides access
to the Internet. Before you can connect to the Internet you must first
establish an account with an ISP.
KILOBYTE
A thousand bytes. Actually, usually
1024 (2^10) bytes.
LAN
Local Area Network. A network that connects
computers in a small pre-determined area (like a room, a building, or a
set of buildings). LAN's can also be connected to each other via telephone
lines or radio waves. Workstations and personal computers in an office are
commonly connected to each other with a LAN. This allows them to have
send/receive files and/or have access to the files and data. Each computer
connected to a LAN is called a node.
MODEM
MOdulator, DEModulator. A device that connects your
computer to a phone line in order to communicate with other computers.
MTU
Maximum Transmission Unit. The greatest amount of data or
"packet" size that can be transferred in one physical frame on a network.
This packet also contains the header and trailer information, which are
like addresses for each packet that are required by the routers on the
network.
PACKET
The unit of data sent across a
network.
PORT
A place where information goes into or out of a
computer.
PROTOCOL
A specification that describes how computers will
talk to each other on a network.
PROXY SERVER
A technique used to cache information on a Web
server and acts as an intermediary between a Web client and that Web
server. This is common for an ISP especially if they have a slow link to
the Internet. Proxy servers are also constructs that allow direct Internet
access from behind a firewall. They open a socket on the server, and allow
communication via that socket to the Internet. For example, if your
computer is inside a protected network, and you want to browse the Web
using Netscape, you would set up a proxy server on a firewall.
QUEUE
A waiting area for files, print jobs,
messages, or anything else being sent from one computer or device to
another. In CuteFTP, for instance, you can put files in the queue, and
transfer them all at once at another time.
SERVER
A computer on a network that answers
requests for information, such as Web servers, FTP servers and secure
servers. The term server is also used to refer to the software that makes
serving information possible.
SPIDER
Also called wanderers or robots (bots), spiders are
programs that search the Internet for new, publicly accessible resources
such as Web pages and files in public FTP archives. Spiders contribute
their discoveries to a database, which Internet users can search by using
search engines such as Lycos or WebCrawler.
TCP/IP
(Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol). A
set of protocols that make TELNET, FTP, e-mail, and other services
possible among computers that aren't on the same network.
WAN
Wide Area Network. A network that connects computers over
a large geographic area.
WAREZ
Widely used to denote cracked or pirate versions of
commercial software. In other words, illegal pirated software.
WILDCARD
A character string that is used in text searches to
make finding a match easier. An asterisk (*) usually means find any
character or set of characters.
ZIP
A Microsoft Windows based compressed (archive)
file. Can contain one or many files as well as a directory structure. On
the Internet, large graphics and programs are usually compressed into ZIP
files and then made available for download. After you download this file
you need to use a decompression software program to "unzip" the
file.
| 
